Luftwaffe Messerschmitt Bf109 Fighter
On 28th May 1935 Willy Messerschmitt Bf 109 prototype flew for the first time. It was a single-seat monoplane fighter. It was powered by a British 695-hp Rolls-Royce Kestrel engine. The second prototype was fitted with German 610-hp Junkers Jumo 210A engine. In 1937 the JG132 ' Von Richthofen' squadron received their first Bf 109B-1 Messerschmitt fighter. They excelled themselves during the Spanish Civil War where their pilots gained vital experience before World War 2. Messerschmitt Bf 109 B, C, D and E versions took part in the Spanish Civil War.
The German Luftwaffe had more than 1,000 Bf 109s in operational service by the time World War Two started in 1939. During the September 1939 German invasion of Poland the Luftwaffe had 850 Bf-109Es and 235 Bf-109Ds. During the "Blitzkrieg Lightning War" about 200 Bf-109s took part 67 were shot down, mostly to ground fire.
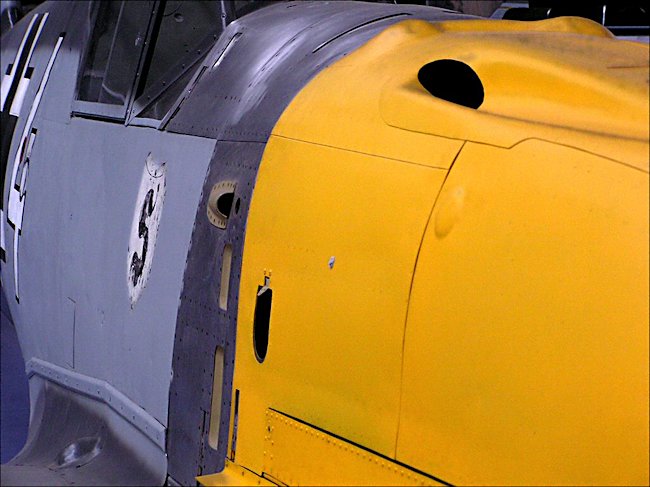

Photograph taken at the RAF Museum, Hendon, London NW9 5LL England
All their Jagdgeswader fighter squadrons were equipped with Bf 109 E (Emil) planes by the start of the Battle of Britain in July to September 1940. Luckily for the RAF in November 1939 a confused Luftwaffe pilot set a Messerschmitt Bf-109E Emil down on the wrong side of the French border. The aircraft was flown back to England where it was tested and put through mock dogfights with British fighters.
The evaluation concluded that the Messerschmitt Bf-109E Emil was superior to the Hawker Hurricane in almost all respects but a match for the three-bladed Supermarine Spitfire Mark I except at high altitude where the Spitfire had an advantage. This particular Messerschmitt is now in the RAF Museum at Hendon.

Photograph taken at the RAF Museum, Hendon, London NW9 5LL England
It is estimated that over 35,000 Messerschmitt fighters have been produced. It had a maximum Speed at 23,000 ft of 385mph, with a ceiling of 38,500 ft. Its normal range was 450 miles. The Messerschmitt Bf-109E-1 was armed with four MG-17 7.9-millimeter machine guns, with two in the cowling and two in the wings. It became the main fighter of the German Luftwaffe for the first few years of World War Two. The Messerschmitts Bf 109 scored more kills than any other aircraft during WW2. The most successful ace during this period was Maj. Erich Hartmann with 352 kills flying a Messerschmitts Bf 109. This is still a world record for one pilot.
The Messerschmitt Bf 109 a more reliable engine which had direct injection fuel system. This meant that it had no problems with negative G-forces. The fighter also had better climbing rates. Most of the 1172 planes belonging to RAF's Fighter Command shot down during the Battle of Britain were victims of the Messerschmitts Bf 109 E. During the same Battle the German Luftwaffe loses were slightly higher. They had 1792 planes shot down, of which 610 were Messerschmitts Bf 109 E-type. The "Bf-109E-3" variant replaced the MG-17 wing guns to MG-FF 20 millimetre cannons with 60 RPG. The bigger weapons dictated fit of a blister in the lower wing. The pilot could choose to fire one or both cannons.
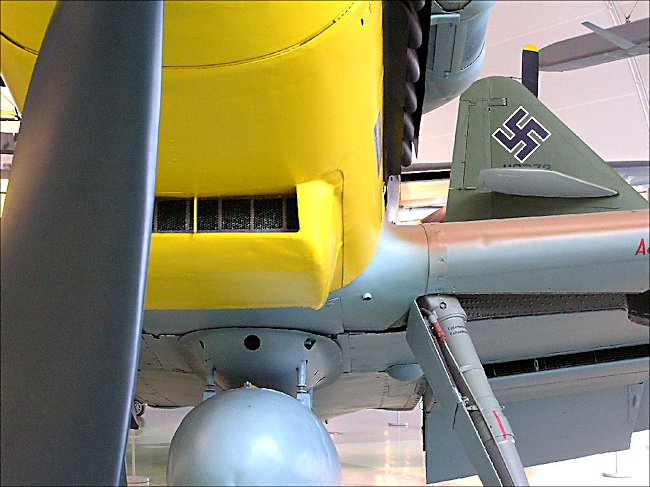
Photograph taken at the RAF Museum, Hendon, London NW9 5LL England
During the Battle of Britain the Messerschmitts Bf-109s were ordered to operate as bomber escorts. This forced them into a defensive posture, which put them at a disadvantage relative to Hurricanes and Spitfires. The limited range was also another problem as it could not stay over the battle area for very long. If a German pilot had to bail out he would spend the rest of the war as a POW. British pilots who had to bail out returned to battle the next day.
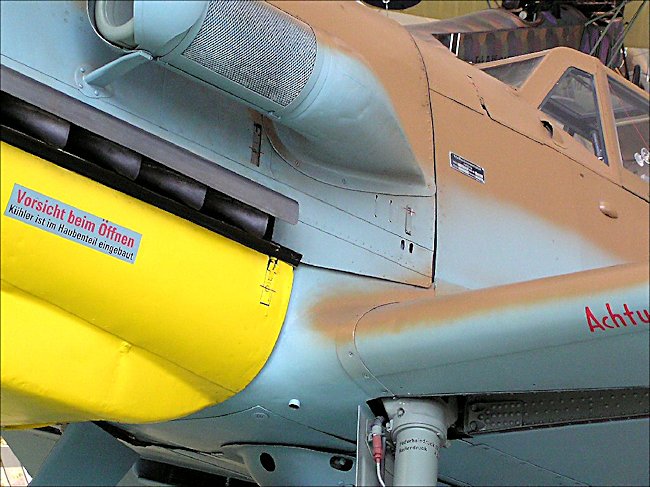

Photograph taken at the RAF Museum, Hendon, London NW9 5LL England
Bf-109E-4 variant but the MG-FF wing cannon were updated to MG-FF/M cannon with a "softened" recoil mechanism to allow it to fire devastating high-explosive "mine" shells. The softened recoil mechanism also resulted in a higher rate of fire. The Messerschmitt Bf 109 F (Fredrik) was the next upgrade version of the plane during 1941 - 42. Only the rear fuselage had not been altered. It was a totally new plane. The Messerschmitt Bf 109 G was introduced during late summer of 1942 and was the backbone of the Luftwaffe to the end of the war.
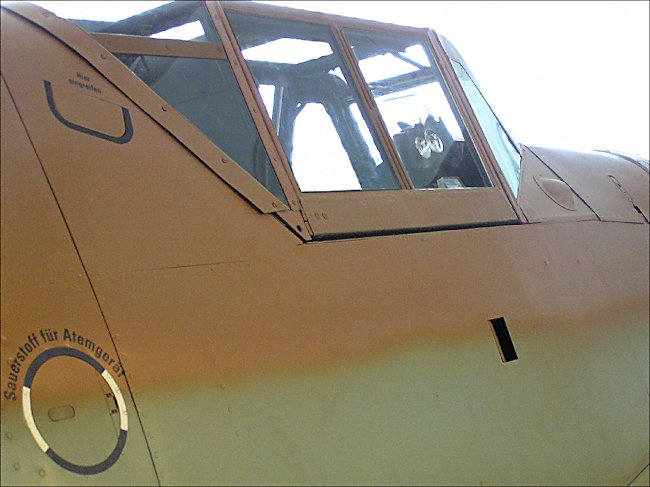

Photograph taken at the RAF Museum, Hendon, London NW9 5LL England
Bf-109E-4 variant but the MG-FF wing cannon were updated to MG-FF/M cannon with a "softened" recoil mechanism to allow it to fire devastating high-explosive "mine" shells. The softened recoil mechanism also resulted in a higher rate of fire. The Messerschmitt Bf 109 F (Fredrik) was the next upgrade version of the plane during 1941 - 42. Only the rear fuselage had not been altered. It was a totally new plane. The Messerschmitt Bf 109 G was introduced during late summer of 1942 and was the backbone of the Luftwaffe to the end of the war.

Photograph taken at the RAF Museum, Hendon, London NW9 5LL England
Messerschmitt Bf109 books


Tweet